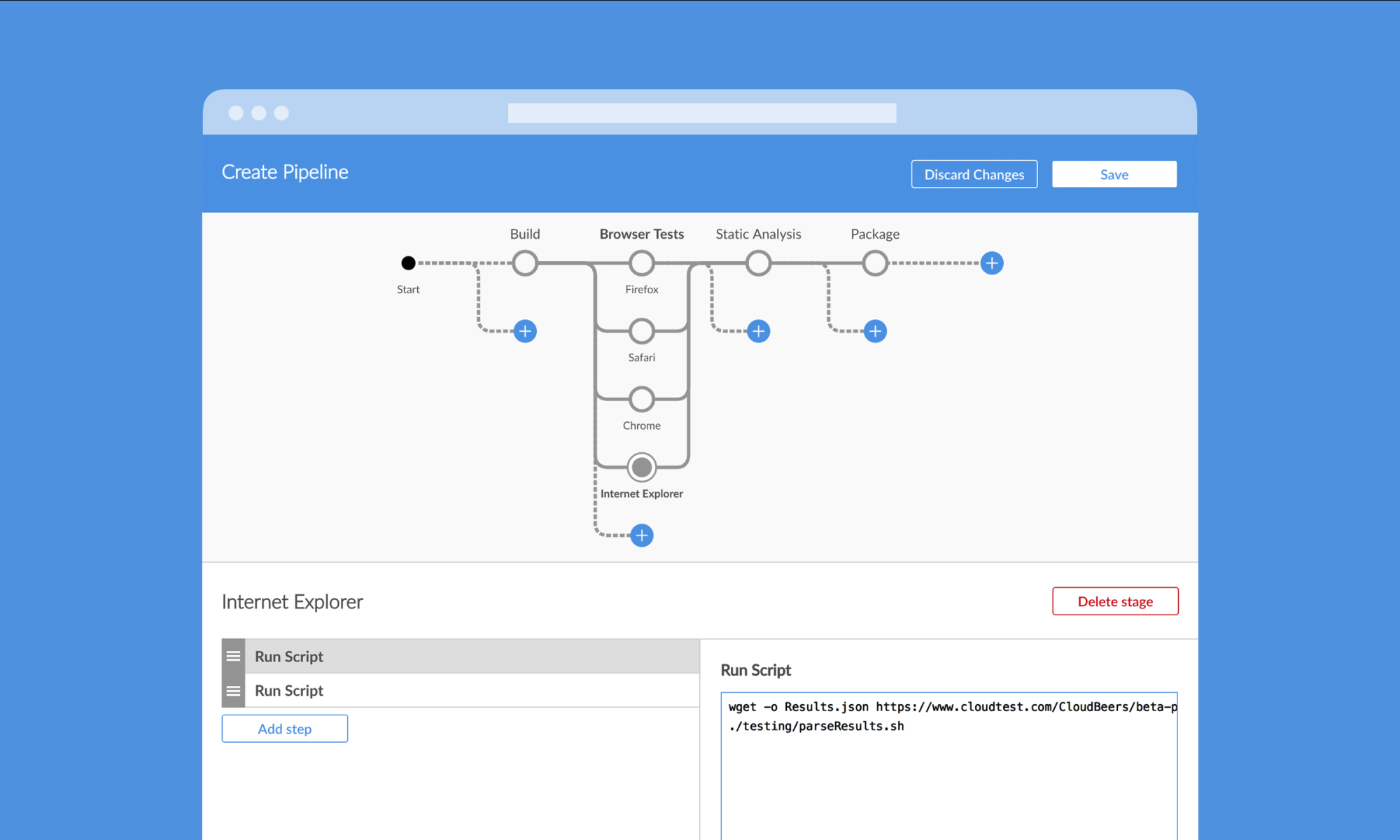
Rosetta World is a social gaming service. TOTALe Mobile Companion is a Rosetta Stone mobile app for iOS and Android devices. With Version 4, Rosetta Stone adds stricter copy protection measures. Rosetta Stone Language Learning 5.0.13. Rosetta Stone released Version 5 on October 9, 2014. Mkdir Chain Next, run the ont-rosetta image using the command specified below. Note that we mount three volumes into the container. The three volumes store log data, block data, and allow access to the host configuration file. The Hosts file is used by the operating system to map human-friendly hostnames to numerical Internet Protocol (IP) addresses which identify and locate a host in an IP network. The hosts file is one of several system resources that address network nodes in a computer network and is a common part of an operating system's IP implementation. C:ProgramDataRosetta StoneSupport My Work on Patreon Donations Welcome. Copy the unlocked files into Rosetta Stone’s installation directory and overwrite (like: C: Program Files (x86) Rosetta Stone Rosetta Stone Language Training) Start Rosetta Stone, if you see the ‘Activation Window‘ asking for a serial number, simply select the ‘Activated Products‘ tab and then click ‘Continue‘ All done, enjoy!
- Block Rosetta Stone Host File
- Rosetta Stone Wall Block
- Block Rosetta Stone Host File Free
- Rosetta Stone Wall
- Block Rosetta Stone Host File Extension
- Block Rosetta Stone Host File Download
(archived 2002-06-07)
| A Sysadmin's Unixersal Translator (ROSETTA STONE)OR What do they call that in this world? | ||||
Contributions and corrections gratefully accepted. Please help us fill in the blanks. New 'tasks' are welcome, too! | ||||
| hardware, firmware, devices | disks | kernel, boot, swap | files, volumes | |
| networking | security, backup | software, patching, tracing, logging | references | |
| TASK OS | AIX | Darwin | Caldera OpenServer | DG/UX | FreeBSD | HP-UX | IRIX | Linux | NetBSD | OpenBSD | Solaris | SunOS 4 | Tru64 | Ultrix | UNICOS | OS / TASK |
| OS notes | The Open Source foundation for Mac OS X, descended from NeXTStep | UnixWare 7.1. Formerly SCO | (rh) = Red Hat, Mandrake, Suse,... (deb) = Debian, Storm, Progeny, Corel,... | Solaris 2.0-2.6, 7, 8, 9 (SunOS 5.*) SVR4-based | Solaris 1.* BSD-based | (Digital Unix, OSF/1) (4)= 4.0F/G (5)= 5.0A | Cray Inc., formed from the March 2000 merger of Tera Computer Company and Cray Research | OS notes | ||||||||
| administrative GUI | smit smitty wsm | Aqua: System Preferences, NetInfo Manager | scoadmin | sysadm | /stand/sysinstall | sam | /usr/sysadm/bin/sysmgr (6.3+) toolchest /usr/Cadmin/bin/* | linuxconf yast2 (Suse) | sushi | solstice | checklist (5) sysman | checklist /etc/install/install xmenu | administrative GUI | |||
| managing users | lsuser mkuser chuser rmuser | Aqua: System Preferences, Users | scoadmin useradd userdel | pw | useradd userdel | /usr/Cadmin/bin/cpeople | useradd userdel | useradd userdel | useradd userdel adduser (interactive) | useradd userdel | xadmin udbgen udbrstrict nu scripts | managing users | ||||
| list hardware configuration | prtconf lscfg lsattr lsdev | ioreg -bls | hwconfig /usr/lib/X11/testtools/ | dg_sysreport -g hardware | dmesg cat /var/run/dmesg.boot | ioscan | hinv | dmesg (if you're lucky) | dmesg more /var/run/dmesg.boot cat /kern/msgbuf | dmesg cat /var/run/dmesg.boot | prtconf -v | dmesg (if you're lucky) | uerf -R -o full dia -R full (5) hwmgr -show devices | uerf -R -o full (if you're lucky) | machid | list hardware configuration |
| show/set EEPROM/NVRAM values | bootlist -o -m normal | nvram | pciconf -l | setboot bootadmin (at boot PROM) stm | nvram printenv/setenv (at command monitor) | /dev/nvram (if you have it) hwclock | eeprom | openprom (on OpenFirmware architectures) | eeprom | (4.0D+) consvar | show/set EEPROM/NVRAM values | |||||
| add device without reboot | cfgmgr -v | (automatic — autdodiskmounter) | mkdev | ioscan -fnCdevtype; | scsiha -pr ioconfig -f /hw | modprobe kerneld insmod | devfsadm. pre-Solaris 7, use: drvconfig; devlinks; {disks, tapes, ports} | (3.2.*) scu scan edt | add device without reboot | |||||||
| tape device | /dev/rmt0 | /dev/rct0 | /dev/rsa0 | /dev/rmt/0 | /dev/tape /dev/nrtape | /dev/st0 | /dev/st0 | /dev/st0 | /dev/rmt/0 | (5.x) /dev/ntape /dev/tape | tpmnt | tape device | ||||
| X kvm config | hwconfig | xf86config | kdmconfig (x86) | X kvm config | ||||||||||||
| read a disk label | lspv -l | Disk Utility | fsname | admpdisk -o list admvdisk -o list | disklabel -r | diskinfo pvdisplay | prtvtoc | fdisk -l | disklabel -r disk mbrlabel | fdisk -r OR disklabel -rl | prtvtoc | dkinfo | disklabel -r | chpt -q | read a disk label | |
| whole disk in partition | N/A | (non-root partitions are mounted under /Volumes) | /dev/1s# (#=0,1,...) | c | 10 | c or d sysctl kern.rawpartition | c | 2 | c | c | c | whole disk in partition | ||||
| label a disk | mkvg | (labels unused) | admpdisk | fdisk disklabel -wr sysinstall | pvcreate | dvhtool | cfdisk fdisk e2label | disklabel -wr mbrlabel | disklabel -wr | format | format | disklabel -rw | chpt -a | /etc/labelit | label a disk | |
| partition a disk | mklv | pdisk | admpdisk | fdisk sysinstall | lvcreate sam | fx | parted (if you have it) fdisk pdisk (on a MAC) | disklabel -i | fdisk -e OR disklabel -E | format fmthard | format | disklabel -e | chpt -p | /etc/install/install | partition a disk | |
| kernel | /unix | /mach_kernel | /unix | /dgux | /kernel | /hpux (9) /stand/vmunix (10+) | /unix | /boot/vmlinuz /boot/bootlx | /netbsd | /bsd | /kernel/genunix /platform/`uname -m`/ kernel/unix /platform/`uname -m`/ kernel/sparcv9/unix (7+) | /vmunix | /vmunix | /vmunix | /unicos | kernel |
| show/set kernel parameters | /usr/samples/kernel/vmtune (installed with the bos adt.samples fileset) /usr/sbin/no (network-related) | /usr/sbin/sysctl | /etc/conf/cf.d/configure -x | /boot/kernel.conf | sam sysdef kmtune (11+) getconf | systune | /proc/* /proc/sys/* | sysctl /etc/sysctl.conf | /etc/sysctl.conf | sysdef | dxkerneltuner sysconfig | show/set kernel parameters | ||||
| show runlevel | who -r | (runlevels unused) | who -r | who -r | who -r | who -r | /sbin/runlevel | N/A | who -r | who -r | who -r | show runlevel | ||||
| make disk bootable | bosboot -a | bless | mkboot | dvhtool | fdisk -A(and lilo to manipulate mbr) | fdisk -i installboot | installboot /usr/platform/ `uname -m` /lib/fs/ufs/bootblk raw_device_file | (4.x+) disklabel -rw -t [ufs|advfs] | make disk bootable | |||||||
| startup scripts | /etc/rc* | /System/Library/ StartupItems/*, /Library/StartupItems/, /etc/rc* | /etc/rc* | /etc/rc* | /etc/rc* /usr/local/etc/rc.d/ | /etc/rc* (9) | /etc/rc* /etc/init.d/ | /etc/rc* (but may vary) /etc/init.d/ | /etc/rc* | /etc/rc* | /etc/rc* /etc/init.d/ | /etc/rc* | /sbin/init.d; links in /sbin/rc?.d | /etc/rc* | startup scripts | |
| check swap space | lsps -a | ls -l /var/vm | swap -l | admswap -o list -buv dg_sysreport -p freeswap | swapinfo | swapinfo | swap -s swap -l | cat /proc/meminfo free | swapctl -l | swapctl | swap -s swap -l | pstat -s | swapon -s | /etc/swapper | check swap space | |
| 'normal' filesystem | jfs | ufs hfs+ | htfs | dg/ux | ufs | hfs | efs, xfs | ext2 ext3 ReiserFS | ffs (was ufs) | ffs (was ufs) | ufs | 4.2 | (4) ufs | ufs | NC1FS C2FS | 'normal' filesystem |
| volume-based filesystem | jfs | vdisk | ccd vinum | jfs (vxfs) LVM VxVM ($) | xlv, xvm, xfs | Linux Volume Manager (LVM) | ccd, raidframe | ccd | Solstice DiskSuite VxVM ($) | Advfs LSM | volume-based filesystem | |||||
| file system description | /etc/filesystems | NetInfo | /etc/mnttab | /etc/fstab | /etc/fstab | /etc/checklist (9) /etc/fstab (10+) | /etc/fstab | /etc/fstab | /etc/fstab | /etc/fstab | /etc/vfstab (local) | /etc/fstab | /etc/fstab AdvFS: /etc/fdmns | /etc/fstab | /etc/fstab | file system description |
| volume manipulation | smitty vg | Disk Utility / pdisk | sysadm | vinum | vg*; lv*; pv* extendfs fsadm | xlv_mgr | e2fsadm lvcreate lvremove lvextend | ccdconfig raidctl | /opt/VRTSvxva/bin/vxva (Veritas) /usr/opt/SUNWmd/ sbin/metatool (DiskSuite) | AdvFS: mkfdmn, mkfset, addvol, showfdmn LSM: volassist or volmake, volume, volplex and volsd, volprint | /etc/install/install | volume manipulation | ||||
| create filesystem | crfs | (automatic) | newfs | mkfs | mkfs | mke2fs | newfs | newfs | newfs mkfs | AdvFS: mkfdmn UFS: newfs MFS: mfs | bb mkfs labelit | create filesystem | ||||
| create non-0-length empty file | lmktemp | dd if=/dev/zero of=filenmae bs=1024 count=desired | dd if=/dev/zero of=filenmae bs=1024 count=desired | truncate -s size[K|M|G] filename dd if=/dev/zero of=filename bs=size[b|k|m|g] count=desired | prealloc | mkfile | dd if=/dev/zero of=filename bs=1024k count=desired | dd if=/dev/zero of=filename bs=1m count=desired | dd if=/dev/zero of=filename bs=1024k count=desired | mkfile | dd if=/dev/zero of=filename bs=1024k count=desired | create non-0-length empty file | ||||
| mount CDROM | mount -v cdrfs -o ro smitty cdrom | (automatic — autdodiskmounter) | mount /dev/cd0 path | mount /cdrom mount_cd9660 /dev/acd0? /cdrom | pfs_mountd pfsd pfs_mount | (mounts automatically when CD inserted) | mount /cdrom | mount /dev/cd0a path | mount -t cd9660 -r /dev/cd0a path | /etc/init.d/vold start; volcheck or mount -F hsfs /dev/sr0 /cdrom | mount /dev/disk/cdromXa /mnt | mount CDROM | ||||
| NFS share definitions | /etc/exports /etc/xtab | NetInfo: /config/SharePoints | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | /etc/dfs/dfstab | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | /etc/exports | NFS share definitions | ||
| NFS share command | exportfs -a | exportfs -a /etc/nfs start | kill -s HUP `cat /var/run/mountd.pid` | exportfs -a | exportfs -a | /etc/init.d/nfs-server reload (rh) exportfs -a | kill -s HUP `cat /var/run/mountd.pid` /etc/rc.d/mountd reload | kill -HUP `cat /var/run/mountd.pid` | share shareall | exportfs -a | /sbin/init.d/nfs start; /sbin/init.d/nfsmount start | exportfs -a | NFS share command | |||
| name resolution order | /etc/netsvc.conf | NetInfo | /etc/host.conf | /etc/nsswitch.conf | 6+: /etc/nsswitch.conf 5.3: /etc/resolv.conf | /etc/nsswitch.conf /etc/resolv.conf | /etc/nsswitch.conf /etc/resolv.conf | /etc/resolv.conf | /etc/nsswitch.conf | /etc/svc.conf | /etc/hosts.usenamed | name resolution order | ||||
| show network interface info | ifconfig -a no -a netstat -i | ifconfig -a | ifconfig -a | ifconfig -A | lanadmin landiag lanscan netstat -in | ifconfig -a netstat -ia | /sbin/ifconfig | ifconfig -a netstat -in | ifconfig -A | ndd ifconfig -a netstat -in (8+) kstat -n hme0 | egrep 'ifspeed|duplex' | ifconfig -a | ifconfig -a netstat -in | show network interface info | |||
| change IP | smitty chinet | System Preferences: Network NetInfo | ifconfig netconfig | sysadm | edit /etc/rc.conf (option ifconfig_interfacename) | /sbin/set_parms initial | edit: /etc/{hosts, sys_id, resolv.conf, TIMEZONE}, /etc/config/ {static-route.options, ifconfig-1.options}; reboot | (rh) edit: /etc/hosts, | edit /etc/ifconfig.interface dhclient | edit /etc/hostname.driver | edit: /etc/{resolv.conf, hosts, hostname.*, netmasks, nodename, sys-unconfig; reboot | (4.x) netsetup (5.x) sysman net_wizard or netconfig | netconfig /etc/install/install | change IP | ||
| ping one packet | ping -c 1 hostname | ping -c 1 hostname | ping -c 1 hostname | ping -s -c 1 hostname | ping -c 1 hostname | ping hostname 10 1 (9) ping hostname -n 1 (10+) | ping -c 1 hostname | ping -c 1 hostname | ping -c 1 hostname | ping -c 1 hostname | ping hostname packetsize 1 | ping hostname packetsize 1 | ping -c 1 | ping hostname | ping one packet | |
| sniff network | iptrace ipreport | nettl | snoop tcpdump | etherfind tcpdump | tcpdump | snoop | etherfind | sniff network | ||||||||
| route definitions | netstat -r smitty route | netstat -r | netstat -r | sysadm | edit /etc/rc.conf (option defaultrouter) | /etc/rc.config.d/netconf | /etc/config/ static-route.options | (rh) /etc/sysconfig/network (rh) /etc/sysconfig/static-routes (deb) /etc/init.d/network (deb) /etc/network | netstat -r route show | netstat -r route show | /etc/defaultrouter /etc/notrouter | /etc/routes | netstat -r | route definitions | ||
| telnetd, ftpd banner | /etc/security/login.cfg | /etc/ftpwelcome | /etc/ftpwelcome | /etc/inetd.conf (telnet) | /etc/issue | /etc/issue.net (telnet) (ftp varies; can use tcp wrappers) | /etc/default/telnetd /etc/default/ftpd | /etc/issue | /etc/issue /etc/motd | telnetd, ftpd banner | ||||||
| encrypted passwords in | /etc/security/passwd | NetInfo | /etc/shadow | /etc/shadow | /etc/master.passwd | /etc/passwd (not Trusted) /secure/etc/passwd (Trusted 9) /tcb/files/auth/ (10+) | /etc/shadow | /etc/shadow (may vary) | /etc/master.passwd (/etc/pwd.db) | /etc/master.passwd (/etc/pwd.db) | /etc/shadow | /tcb/files/auth (only with Enhanced Security) | /etc/shadow | /etc/udb | encrypted passwords in | |
| allow/deny root logins | /etc/security/user | /etc/ttys (doesn't affect ssh) | /dev/default/login | /etc/default/login | /etc/login.access; /etc/ttys | /etc/securetty | /etc/default/login | /etc/securetty | /etc/ttys | /etc/ttys | /etc/default/login | /etc/securettys | udbrestrict -R | allow/deny root logins | ||
| show installed software | lslpp -L | ls /Applications Apple System Profiler | swconfig | pkginfo | pkg_info | rmfn, what (HP-UX 9) swlist (HP-UX 10+) | versions | (rh) rpm -a -i (rh) rpm -qa (deb) dselect (deb) dpkg -l | pkg_info | pkg_info | pkginfo prodreg admintool | setld -i | show installed software | |||
| add software | smitty install_all /usr/lib/instl/sm_inst | drag-and-drop | custom | /stand/sysinstall /usr/ports make pkg_add | swinstall | inst swmgr | (rh) rpm -hiv (deb) dselect (deb) apt-get install pkg (deb) dpkg -i | pkg_add /usr/pkgsrc && make | pkg_add /usr/ports && make | pkgadd | setld -l | add software | ||||
| precompiled binaries of GPLware and freeware | aixpdslib.seas.ucla.edu/ aixpdslib.html www-frec.bull.com/ docs/download.htm | fink.sourceforge.net | www.caldera.com/ skunkware | ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/.0/ FreeBSD/ports/i386/ packages-4.0-release | www.linux.org linux.tucows.com | ftp://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/ NetBSD/packages | ftp://ftp.openbsd.org/ pub/OpenBSD/<version>/ packages | www.sunfreeware.com | www.tru64unix.compaq.com/ demos tpegsrvr.zk3.dec.com/ freeware/tbl_packages.html | precompiled binaries of GPLware and freeware | ||||||
| C compiler | /usr/ibmcxx/bin/cc | /usr/bin/cc (hacked gcc) | /usr/bin/cc | /usr/sde/default/usr/bin/cc | /usr/bin/cc (gcc) | /opt/softbench/bin/cc ($) /bin/cc (9) /usr/bin/cc (10+; not ANSI; kernel builder only) | /opt/MIPSpro/ bin/cc ($) /usr/bin/cc | gcc | /usr/bin/cc | /usr/bin/cc | /opt/SUNWspro/ bin/cc ($) | /usr/bin/cc | /usr/bin/cc | /opt/ctl/bin/cc | C compiler | |
| show patch level and/or patches | instfix -ivq | Apple:About This Mac ls /Library/Receipts | swconfig -P | uname -a | swlist -l product | grep someString | versions -b | grep patch (6.4-) | (rh) rpm -q (deb) dpkg -s | cat /kern/version uname -a | showrev -p prodreg (2.6+) patchadd -p | dupatch -track -type kit dupatch -track -type patch setld -i | grep patchname | show patch level and/or patches | |||||
| patch tool | installp smitty update_all | System Preferences / Software Update | dg_sysreport -p patches | (cvsup or cvs to update, then rebuild) | update (9) swinstall (10+) | inst | (deb) apt-get update (deb) apt-get upgrade | cvs | cvs/CTM | installpatch (2.5.1-) patchadd (2.6+) pkgadd /usr/sadm/bin/smpatch (9+) | setld -i dupatch | patch tool | ||||
| configure/show runtime linking | chatr | ldconfig ldd | crle ldd pldd | configure/show runtime linking | ||||||||||||
| link library path | $LIBPATH | $SHLIB_PATH | $LD_LIBRARY_PATH | $LD_LIBRARY_PATH | $LDPATH | link library path | ||||||||||
| tracing utility | trace syscalls truss | ktrace | ktrace truss ltrace | trace (freeware) tusc (11+, freeware) | par | strace | ktrace ktruss | ktrace ptrace | truss sotruss | trace | trace truss | cdbx jumptrace | tracing utility | |||
| define user defaults | /etc/default/login | /etc/profile /etc/security/ | /etc/default/login /etc/profile /etc/security/ | udbgen nu scripts | define user defaults | |||||||||||
| csh global .login | /etc/csh.login | /etc/csh.login | /etc/cshrc | /etc/csh.login | /etc/.login | /etc/login | csh global .login | |||||||||
| default syslog | /var/adm/syslog | /var/log/system.log | /usr/adm/syslog /var/adm/log/osmlog | /var/adm/messages | /var/log/messages | /var/adm/syslog/syslog.log | /var/adm/SYSLOG | /var/log/syslog /var/log/messages | /var/log/messages | /var/log/messages | /var/log/syslog | (4.x+) /var/adm/messages /var/adm/syslog.dated (kern, auth, daemon, lpr, syslog, user) /var/adm/binary.errlog | /usr/adm/messages | default syslog | ||
| system error reporting tool | errpt | Console /var/log/crash.log, dmesg | dmesg | admsyslog -o report | dmesg | dmesg sysdiag (9 and early10) stm/cstm/mstm/xstm (10.20+) | sysmon amsyslog availmon eventmond imdmonitor syserrpanel | dmesg | dmesg cat /kern/msgbuf | dmesg | prtdiag | dmesg | (4.x) uerf; dia (DECevent) (5.x) (System errors) EVM (evmget; evmshow) (Hardware errors) dia; ca (Compqaq analyze) | uerf | errpt | system error reporting tool |
| performance monitoring | ftp://ftp.software.ibm.com/ aix/tools/perftools/perfpmr | vm_stat nfsstat Process Viewer | fstat; nfsstat; systat; vmstat; netstat; sockstat; uustat; top | pcp dkstat pmkstat | vmstat | iostat; netstat; systat; vmstat | iostat; pstat; systat; vmstat | sar; iostat; kstat; | /usr/opt/sv4b/bin/sar | sar; xsar; tsar; xsam; | performance monitoring | |||||
| FAQs (see also faqs.org) | www.faqs.org/faqs/ aix-faq/part1/ preamble.html | www.darwinfo.org/ faq.shtml | pcunix.com/SCOFAQ/ | www-csc.dg.com/csc/ dguxfaqs1.asp | www.freebsd.org/doc/ en_US.ISO8859-1/books/faq | www.faqs.org/faqs/ hp/hpux-faq/preamble.html | techpubs.sgi.com/library/ tpl/cgi-bin/browse.cgi?coll=0650 &db=FAQ | www.linuxdoc.org/ FAQ/Linux-FAQ | www.netbsd.org/ Documentation | www.openbsd.org/faq | www.faqs.org/faqs/Solaris2/ FAQ/ www.faqs.org/faqs/Solaris2/ x86/FAQ/ | www.faqs.org/faqs/ comp-sys-sun-faq/ | www2.tru64.org/faq/ tru64_faq.php | www.supelec.fr/decus/ faq/faq-ultrix.html | www.spikynorman .net | FAQs (see also faqs.org) |
| mailing list | AIX-L@pucc. princeton.edu (LISTSERV) | lists.apple.com | www.freebsd.org/ handbook/ eresources.html #ERESOURCES-MAIL | hpux-admin@ dutchworks.nl (majordomo) | www.netbsd.org/ MailingLists | www.openbsd.org/ mail.html | sun-managers@sunmanagers .org (majordomo) | sun-managers@ sunmanagers .ececs.uc.edu (majordomo) | tru64-unix-man agers@ornl.gov (majordomo) http://www.ornl.gov/its/archives/ mailing-lists/ | decstation-man agers@ornl.gov (majordomo) | mailing list | |||||
| mailing list archives | lists.apple.com | www.freebsd. org/ search.html# mailinglists | www.dutch works.nl/ htbin/hpsysadmin | www.linuxmanagers.org/ pipermail/linuxmanagers | www.netbsd.org/ MailingLists | www.openbsd.org/ mail.html | www.latech. edu/sunman.html | www-archive. ornl.gov:8000 | www-archive. ornl. gov:8000 | mailing list archives | ||||||
| newsgroup(s) groups.google | comp.unix.aix www.thp.uni-duisburg.de/ cuaix/cuaix.html | comp.unix.sco.misc | comp.unix.bsd. freebsd.misc | comp.sys.hp.hpux | comp.sys.sgi.admin | comp.os.linux.* (esp .answers) | comp.unix.bsd. netbsd.misc | comp.unix.bsd. openbsd.misc | comp.sys.sun. admin, comp.unix.solaris | comp.sys.sun admin | comp.sys.dec, comp.unix.tru64 | comp.unix.ultrix | comp.unix.cray | newsgroup(s) | ||
| user groups | www.userblue.org | www.apple.com/ usergroups | www.freebsd.org/ support.html#user | www.interex.org | www.deadly.org | Encompass/DECUS | www.cug.org www.excray.com | user groups | ||||||||
| magazines | www.macworld.com | www.daemonnews.com | www.hpchronicle.com www.interex.org/hpuxusr www.hppro.com | www.sgi.com/support/ pipeline.html | www.linuxjournal.com www.linux-mag.com | www.daemonnews.com | www.sunworld.com/ | www.tru64.org/ | magazines | |||||||
| vendor home page | www.developer.ibm.com/ tech/map/aixrm.html | www.apple.com | www.caldera.com/ products/openserver | www.freebsd.org | www.unixsolutions.hp.com/ products/hpux | www.sgi.com/software/ software.html#IRIX | www.linux.org www.redhat.com | www.netbsd.org | www.openbsd.org | www.sun.com/solaris/ | www.tru64unix .compaq.com/ | www.supelec.fr/decus/ faq/faq-ultrix.html | www.cray.com | vendor home page | ||
| vendor docs and patches | www.apple.com/support/ security/security.html | www.caldera.com/support | www-csc.dg.com/csc/ custdocsasp/ custdocs2.asp? category=069docs.asp | www.freebsd.org/handbook www.freebsd.org/releases/ 4.0R/errata.html | techpubs.sgi.com www.sgi.com/ support/patch_intro.html support.sgi.com relnotes grelnotes | www.linuxdoc.org/ rpmfind.net/linux/RPM | www.netbsd.org/ Security | www.openbsd.org/ docum.html | docs.sun.com sunsolve.sun.com | www.tru64unix .compaq.com/docs/ | www.cray.com/ craydoc | vendor docs and patches | ||||
| vendor phone (US) | AIX: 800-237-5511 IBM hardware: 800-426-7378 | 1-800-MY-APPLE | 925-674-0783 (FreeBSD Mall) | 800-633-3600 | 800-800-4SGI | 800-USA-4SUN | 800-344-4825 | 800-344-4825 | vendor phone (US) | |||||||
| TASK / OS | AIX | Darwin | Caldera OpenServer (UnixWare 7.1) formerly SCO | DG/UX | FreeBSD | HP-UX | IRIX | Linux | NetBSD | OpenBSD | Solaris | SunOS | Tru64 (Digital Unix, OSF/1) (4) 4.0F/G (5) 5.0A | Ultrix | UNICOS | OS TASK |
Universal Command Guide is a large book which covers several of the OSs in this table. See http://www.allcommands.com
See also Heiner Steven's AWK dialects page at http://www.shelldorado.com/articles/awkcompat.html
This page is http://bhami.com/rosetta.html last updated 2002.05.31. This compilation Copyright © 2000-2002 Bruce Hamilton bhami@pobox.com. Reproduce freely for personal use. Do not reproduce for commercial purposes. LINK don't copy, or you will miss updates!
The vast majority of third-party applications on your computer can access the internet – and they tend to do so for different reasons. However, there are times when you do not want a specific app to use the internet. In such moments, you may be looking to make changes to your computer settings to prevent the application from reaching the web. Well, in this guide, we intend to show you how to block a program from connecting to the internet.
Why would I want to stop an application from using my internet?
Since you came to this page, you probably have your reasons for wanting to cut off web access for an app. Or perhaps, you got curious while wondering why anyone would want to block an application from accessing the internet in the first place. If our assumptions on the latter hold true, then you are about to find out why people try to prevent programs from using the internet.
For example, you might encounter or use an application that insists on fetching updates and installing them (automatically), but you do not want the updates because they break some functions or cause the app to perform worse than before. In such a scenario, you would not have much choice but to cut off internet access for the program. If the program won’t listen to your instructions to hold off updating itself, then you have to ensure it never gets the updates in the first place.
Here’s another scenario: You might have a game that is suitable for your child only in offline mode, or you do not feel comfortable with your ward getting exposed to online (and unsupervised) multiplayer elements. In that case, you are better off instructing Windows to block internet access for that specific game application to ensure the game remains offline.
Or you might be using an application that spams you with obnoxious ads and are looking for a way to stop the ads from showing up in the first place. Well, since the application needs the internet to fetch the ad data, you can prevent the ad spam by cutting off web access for the app.
In some scenarios, you might come across an application that you suspect to be malicious or harmful. To minimize the risks, it makes sense for you to block such an app from using the internet on your computer. A malicious program that is dependent on the internet to work will struggle to do damage on your computer if it is prevented from reaching the web (and contacting its creators or controllers).
How to block an application from accessing the internet in Windows 10?
Regardless of the reasons you have in mind for wanting to stop an application from using the internet on your computer, the procedure involving the Windows Firewall provides the ideal path for you to achieve your goal. Here, you get to tell Windows what it must do when the application tries to connect to the internet by creating a rule.
Since you want Windows to stop the application from reaching the web, you will have to create an outbound rule to enforce the internet blockage. We will now show you how to do that.
Create a Windows Firewall rule to block internet access for the application:
Go through these steps carefully:
- First, you have to get to the Windows Start menu or screen. You can do it by clicking on the Windows icon in the bottom-left corner of your device’s display.
Alternatively, you can get to the Windows Start menu by hitting the Windows logo icon on your machine’s keyboard.
- Now, you must type Control Panel into the text box (that comes up the moment you begin to type) to perform a search task using those keywords as the query.
- Assuming Control Panel (App) has now emerged as the main entry on the results list, you have to click on it to open the needed application.
- Once the Control Panel window comes up, you have to set the View by parameter (in the top-right corner) to Large icons.
- Now, you have to click on Windows Firewall.
- Assuming you are now on the Windows Firewall menu, you have to look at the list in the top-left corner of the window and then click on the Advanced settings link.

The Windows Firewall with Advanced Security utility window is supposed to come up now.
- Look to the top-left corner of the application window. Click or double-click on Outbound rules.
- Now, you must look to the top-right corner of the program window. Under the Actions panel, you have to click on New rule.
- Click on the radio button for Program (to select this option).
(You are looking to block a program from reaching the internet, after all).
- Now, you have to navigate to the folder where the application you are looking to block is installed. Click on the Browse button and continue the work from there.
Once you specify the application’s folder, the app file path will be displayed automatically. The application path in Windows is usually in the form “C:Program FilesNameOfApp.exe” or “C:Program Files(x86)NameOfApp.exe”, where NameOfApp is the name of the application for which you want to block internet access.
- Once the file path for the program gets specified, you have to click on the Next button to proceed to the next stage.
- On the screen that follows, which should be Action, you have to click on the radio button for Block the connection.
- Click on the Next button.
- On the Profile screen, you have to select all the parameters there (Domain, Private, and Public).
Domain is the rule that applies when your computer gets connected to a domain; Private is the rule that applies when your PC is connected to a private network, which could be your home or office network; Public is the rule that applies when your system is connected a public network, such as the WIFI in a coffee shop or airport.
Well, you need Windows to apply the proposed rule for all the profiles, networks, and setups used by the application. Therefore, all the parameters there have to be selected.
- Click on the Next button.
- Assuming you are now on the Name screen, you have to fill the box for Name with your preferred name for the rule.
Ideally, you should use an easily identifiable name.
- You can also fill the text box for Description – if you like. The task here is optional.
- Click on the Finish button.
Block Rosetta Stone Host File
The rule you just created is supposed to appear on the list under Outbound Rules now. You can check for it there to confirm things.
If you did everything correctly, then Windows will have configured a layer to block all outbound communications from the application for which you want to cut off web access. In most cases, this is usually enough to prevent the app from reaching the web.
Nevertheless, if you want to tighten your grip on the application, then you can go a step further to repeat the same process using Inbound Rules to provide specific instructions to Windows to block all inbound communications for the app. The new rule will be quite identical to the previous one (that you already created), but it will govern inbound traffic for the application in view.
If Windows is already configured to stop an application from sending out data packets in the first place, then the application is unlikely to receive anything from the web. In other words, when the rule for Outbound communication is already configured, the one for Inbound communication is probably overkill (and not needed).
If you want to see how effective the firewall rules can be, then you can run a simple test. You can create an outbound rule to block connections for your browser application to see what happens. After you create the rule, you must open your browser and then try to surf the web (by going to a site or page). If the operation fails and your browser informs you that it cannot connect to the website or internet, then you will know the rule you created has had the effect it should.
You are always free to disable or delete a rule – if you change your mind on the blocking of internet access for a specific application. All you have to do is go through the same steps above to open the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security application, locate the rule under the required section (Inbound or Outbound list), and then perform the required task on the rule.
Other ways of blocking programs from connecting to the internet
Here, we intend to describe alternative methods through which you get to stop an application from reaching the internet. There are scenarios where the proposed procedure involving the creation of rules (in Windows Firewall) just doesn’t cut it.
Take certain games, for example. It might seem that all you need to do is create a blocking rule for NameOfGame.exe, but in reality, that NameOfGame.exe is simply the launcher (executable used to open the application) and the actual connection operations are executed through Java.
In the described scenario, you will need to create a rule to instruct Windows to block connections for Javaw.exe (and not NameOfGame.exe). Or perhaps, you do not even know if the game runs through Java or any similar component, which means you have to start worrying about variables that you failed to account for because you know nothing about them.
Well, given the situation of things (in any of the descriptions provided), you might be better off blocking internet access for the application through one of the following methods.
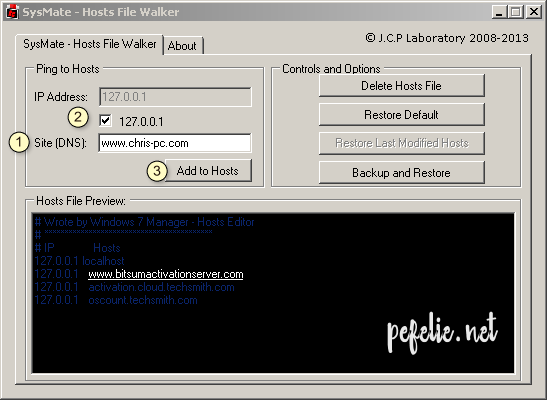
Alter the system host file to block internet access for a specific address or IP:
Here, we intend to show you how to block a program from reaching the internet when the web address or IP address that it connects to is known. For example, if you want your kids to surf the web on a specific browser but do not want them visiting certain sites, then you are likely to find the procedure here useful.
The Windows hosts file is the file that the operating system (running on your machine) employs to manage hostnames and IP addresses. You can add websites to the entries there, and Windows will get specific instructions to block access to those sites automatically.
Anyway, these are the instructions you must follow to do the work here:
- First, you have to open the File Explorer application by clicking on the program icon (which is probably on your taskbar).
Alternatively, you can use the Windows logo button + letter E keyboard shortcut to open the File Explorer app quickly.
- Once the File Explorer window comes up, you have to click or double-click on This PC to see its contents.
- At this point, you have to navigate through the directories on this path:
C:/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts
- Now, in your current location, you have to locate the hosts file and then double-click on it to open it.
Windows is supposed to bring up a small window or dialog asking you which application you want to use to open the file.
- From the list programs displayed, you have to choose Notepad.
The hosts – Notepad window will be displayed.
You are supposed to see something like this:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
# space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a ‘#’ symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 104.54.95.97 testwebpageorsite.com # source server
# 39.23.63.11 testwebpageorsite.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
#127.0.0.1 localhost
#::1 localhost
- Now, under the last # character, you have to type the website URL and IP address for which you want to block internet access.
- Assuming you are done modifying the hosts file, you now have to save the changes you made.
- Look at the top-left corner of the Notepad window, click on the File button there (to see the menu options), and then click on Save.
Alternatively, you can use the Ctrl + letter S keyboard shortcut to instruct Windows to save the changes made to the hosts file.
Block internet access for an app using Parental Control:
Here, you get to block web access for specific applications or websites through the Parental Control feature in Windows. The internet blockage procedure here is suitable for parents who are looking to restrict the applications (especially games) used by their kids or to stop children from accessing certain websites.
These are the instructions you must follow to implement and use Parental Control (to block internet access):
- First, you have to open the Settings application. The Windows logo button + letter I keyboard shortcut will come in handy here.
- Once the Settings window appears, you have to click on Account (to enter the menu for this option).
- Look at the menu list on the left border of the window and then click on Other people.
- Now, you must look to the pane on the right border of the window and then click on the Add a family member option.
- Click on the radio button for Add a child (to select this option) and then click on the Next button.
The new profile for the child will appear now (under the Your family section).
- Click on the Manage family settings online link.
You will be directed to the webpage for the Microsoft parental control for your account. There, you will see all the adult and child accounts that exist on your computer.
- Now, you have to check the top-right corner of the page for Check recent activity. Click on this link.
You will now be directed to the Content Restriction tab or screen. There, you will be able to specify or apply different restriction settings to parameters for the internet and applications.
- Now, you have to specify the games and websites you want to block.
- Save the changes – if this step applies.
Block internet access by disabling the network adapter:
If you are hell-bent on stopping an application from connecting to the internet and do not mind cutting off web access for other programs, then the procedure here is ideal for you. In fact, the proposed method of blocking internet access is probably the most effective of the lot since it requires you to put down the internet connectivity components.
By disabling your computer’s network adapters, you get to block internet access for all utilities or setups on your computer. This method is as fool-proof as it gets.
Rosetta Stone Wall Block
Go through these steps to disable the network adapter:
- Open the Run app by right-clicking on the taskbar (at the bottom of your display) and then selecting Run.
Alternatively, you can use the Windows logo button + letter R keyboard shortcut to do the same thing.
- Once the Run window comes up, you have to fill the field there with msc and then hit the Enter button on your PC’s keyboard (to run the code).
The Device Manager application window will come up.
- Now, you must go through the list of categories, locate Network adapters, and then click on the expansion icon for that category.
The devices inside the Network adapters category will be visible now.
- At this point, you must locate the device through which your computer connects to the internet.
If your PC connects to the web through a WIFI network, then you have to disable the WAN ports. If you use an ethernet cable to connect your computer to the web, then you have to disable the Ethernet connection device. Ideally, you should disable all the devices under the Network adapters category to ensure nothing gets left out.
- To disable a network device, you have to click on it (to get it highlighted), do a right-click on it to see the options available, and then choose Disable device.
- Perform the disabling task on the appropriate devices (or on all the devices, preferably).
Block Rosetta Stone Host File Free
If you change your mind on the internet restrictions you imposed on your computer and decide to do away with them, then you have to do this: go through the same steps above to locate the network devices, right-click on a device to see the standard options list, and then choose Enable device. Basically, to regain internet access, you will have to perform the enabling task for all the devices you disabled earlier. If your internet does not come back on immediately, then you have to restart your PC.
TIP:
Protect PC from Threats with Anti-Malware
Check your PC for malware your antivirus may miss and get threats safely removed with Auslogics Anti-Malware
Rosetta Stone Wall
Block Rosetta Stone Host File Extension
Since you are looking to restrict internet access on your computer, we have reasons to believe your goals are centered around keeping your computer safe or protecting someone from harm. To this end, you may want to beef up your PC’s security by installing Auslogics Anti-Malware.Block Rosetta Stone Host File Download
With the recommended application, you get to force through improvements in your computer’s defense apparatus, regardless of its state currently (whether you have an antivirus running or not). With the projected improvements, the chances of your system falling to malicious programs (or you becoming a victim of a cyberattack) get reduced considerably.